Goniobasis or "Elimia" castanea
> Habitat & Distribution
Goodrich (1940) gave that the range of P. laqueata (in its strict sense) as the Green River and tributaries in Kentucky, tributaries of the Cumberland River in Middle Tennessee, the Duck River and branches, and "tributaries of Tennessee River in Tennessee and Alabama." Our modern surveys would expand that range slightly, to include upper tributaries of the Kentucky River. We would also clarify that P. laqueata does not range upstream in the Tennessee drainage east beyond the vicinity of Chattanooga.
Isaac Lea described Melania castanea from Maury County, TN, in the upper Duck River drainage. Goodrich (1940 lowered the taxon to subspecific level under Goniobasis laqueata, again giving its range as "Headwaters of the Duck River, Tennessee." Our modern surveys have uncovered seven populations in Middle Tennessee, now identified as Pleurocera laqueata castanea, scattered across minor tributaries of the Cumberland, the Harpeth, and the Red River, as well as in tributaries of the upper Duck. We have also identified 14 populations in North Alabama, mostly in the lower Elk drainage, and in small, direct tributaries of the Tennessee River itself.All seven populations inhabit rocky riffles in small to moderate-sized rivers and streams. Considered together with the typical form P. laqueata laqueata and the big-river form P. laqueata alveare, its FWGNA incidence rank is I-5.
> Ecology & Life History
Grazing by populations of pleurocerids can have a significant effect on energy flow in small streams (Dillon 2000: 86 - 91, see also Dillon & Davis 1991).
Like other pleurocerids, P. laqueata is dioecious, eggs being deposited on hard substrates from spring to mid-summer. Eggs are spirally arranged in masses of 2-15 or more, with a tough, membranous outer covering to which sand grains typically adhere (Smith 1980, Jokinen 1992). Although we are unaware of any study specifically directed toward the life history of P. laqueata, it seems reasonable to expect that two years will be required for maturity, and that several years of iteroparous reproduction can be expected thereafter, as is the case for pleurocerids generally (Dazo 1965). This is life cycle Hi of Dillon (2000: 156 - 162).
> Taxonomy & Systematics
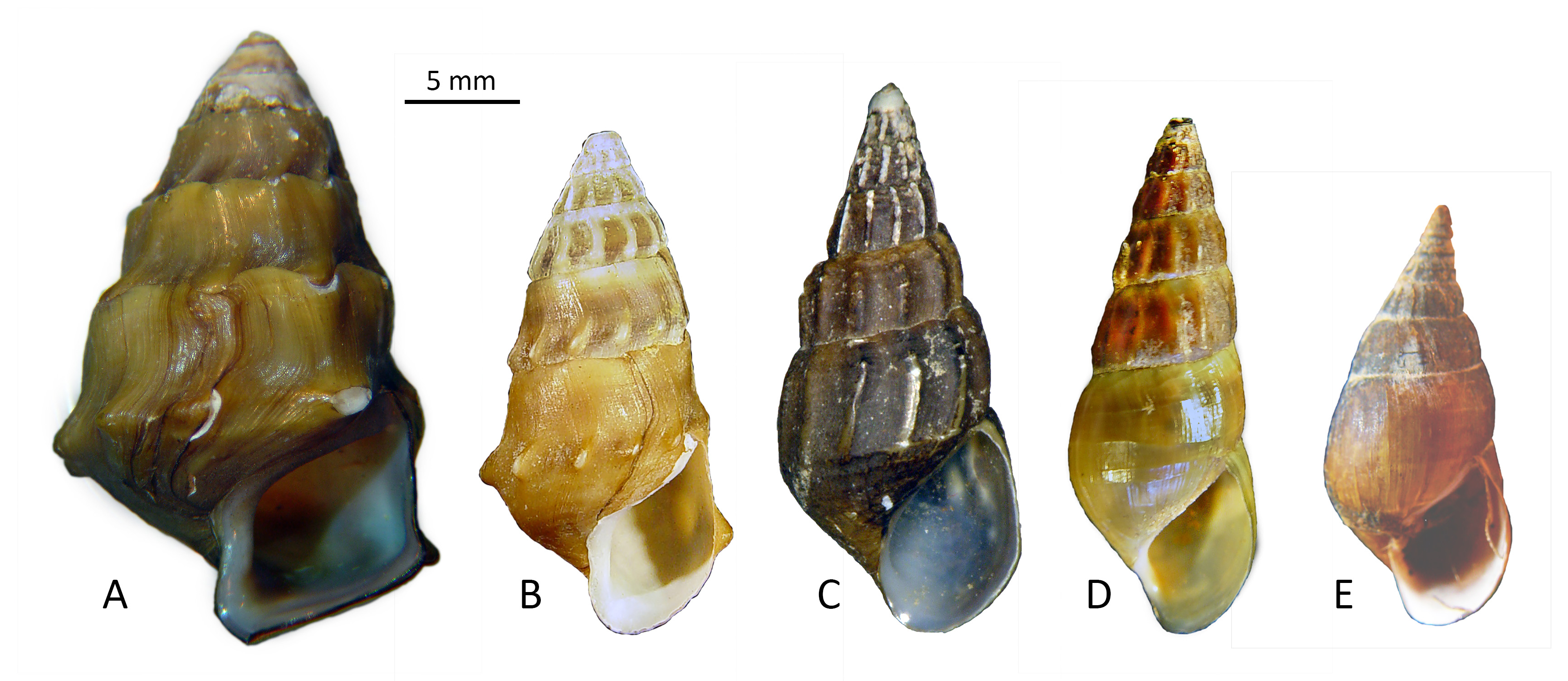
Pleurocera laqueata is another North American pleurocerid species demonstrating protean variability in shell morphology, named and re-named dozens of times in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. Goodrich (1940) recognized ten valid species and six valid subspecies in his group of Goniobasis laqueata, along with no fewer than 55 synonyms. See my essay of 18Sept24 from the link below for a nice photo of intrapopulation variation in shell plication.
The range of typical P. simplex was given by Goodrich (1940) as "headwaters of Tennessee River system in Virginia, Tennessee and North Carolina; Beaver Fork of Bluestone River of Kanawha River, Mercer County, West Virginia," extending no further west than Chattanooga. Our broader surveys and improved understanding of the taxon have revealed a much larger range to the west, however, across the entire Tennessee/Cumberland drainage to its mouth at the Ohio, plus the Green River drainage in Kentucky.
In these regions P. simplex populations inhabiting larger streams often come into contact with P. laqueata. We hypothesize that occasional hybridization between P. simplex and P. laqueata yields progeny bearing shells with very light plications around the apex, which we follow Goodrich in identifying as the subspecies P. laqueata castanea. Lea's (1845) torta is a junior synonym. See my essays of 12Nov24, 10Dec24, and 14Jan25 from the links below for a complete taxonomic review.
There is also strong evidence that populations of P. laqueata hybridize with P. troostiana, yielding a wealth of shell variants identified under that specific nomen as well. See my essay of 15Oct24. We have suggested that Isaac Lea's (1838ish) nomen troostiana (with several subspecies) be applied to populations bearing shells with any degree of striation, leaving Thomas Say's (1829) nomen laqueata for populations bearing shells entirely unstriate.
> Maps and Supplementary Resources
- Pleurocera laqueata in the drainage of The Ohio (2019)
- Distribution in the Tennessee/Cumberland (2022)
> Essays
- Taxonomic controversy has surrounded the generic nomina Pleurocera, Goniobasis, and Elimia for many years. The best entry into the subject would be my essay of 23Mar11, entitled Goodbye Goniobasis, Farewell Elimia. Links are available from that essay to older resources.
- I reviewed the evidence that P. alveare may be a downstream ecophenotypic morph of P. laqueata in my essay of 8Aug18, Pleurocera alveare: Another case of CPP?
- In my essay of 18Sept24 I restricted The Type Locality of Melania laqueata to Browns Creek in Nashville, TN. That essay also includes a nice figure illustrating intrapopulation variance in shell plication.
- See my essay of 15Oct24 for shell morphometric evidence of Widespread hybridization between P. laqueata and P. troostiana in streams of the Tennessee/Cumberland.
- And in my follow-up essay of 12Nov24, I generalized evidence of hybridization between populations of P. laqueata and both P. troostiana and P. simplex to suggest Reticulate evolution in the North American Pleuroceridae. That November essay also featured additional systematic, taxonomic, and biological backround about P. laqueata castanea, including a reproduction of Isaac Lea's original (1843) figure.
- Given the extensive three-way hybridization documented in the essays linked above, we should not be surprised to discover that a wonderful tower of taxonomic babel has been erected to capture the rich variety of shell morphological variation associated. See my review of 10Dec24, Taxonomy Part I, for an image of Lea's castanea holotype and my review of 14Jan25, Taxonomy Part 2, for a discussion of its junior synonym, torta, with images.
> References
Dazo, B. C. (1965) The
morphology and natural history of Pleurocera
acuta and Goniobasis
livescens (Gastropoda: Cerithiacea: Pleuroceridae).
Malacologia 3: 1 - 80.
Dillon, R. T., Jr. (2000)
The Ecology of Freshwater Molluscs. Cambridge, Cambridge University
Press. 509 pp.
Dillon, R. T., Jr. (2011)
Robust shell phenotype is a local response to stream size in the genus Pleurocera.
Malacologia 53: 265-277. [pdf]
Dillon, R. T.,
Jr. (2014) Cryptic phenotypic plasticity in
populations of the North American freshwater gastropod, Pleurocera semicarinata.
Zoological Studies 53:31. [html] [pdf]
Dillon, R. T. Jr.,
& K. B. Davis (1991)
The diatoms ingested by freshwater snails: temporal, spatial, and
interspecific variation. Hydrobiologia 210: 233-242.
Dillon, R. T., Jr., S. J.
Jacquemin & M. Pyron (2013) Cryptic phenotypic
plasticity in populations of the freshwater prosobranch snail, Pleurocera canaliculata.
Hydrobiologia 709: 117-127. [html] [pdf]
Goodrich, C. (1940)
The Pleuroceridae of the Ohio River drainage system. Occas.
Pprs. Mus. Zool. Univ. Mich., 417: 1-21.
Jokinen, E.H. (1992)
The freshwater snails of New York State. New York State Museum
Biological Survey, New York State Museum Bulletin 482.
Lea, Isaac (1838-39) Description of New Freshwater and Land Shells. Transactions of the American Philosophical Society (New Series) 6: 1 154.
Lea, Isaac (1841)
Continuation of Mr. Lea's paper on New Fresh Water and Land
Shells. Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society 2: 11
15.
Lea, Isaac (1843)
Description of New Fresh Water and Land Shells. Transactions of
the American Philosophical Society (New Series) 8: 163 250.
Lea, Isaac (1845) Descriptions of new fresh water and land shells. Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society 4: 162 168.
Lea, Isaac (1848) Description of new fresh water and land shells. Transactions of the American Philosophical Society 10: 67 101.
Say, T. (1829) Descriptions
of some new terrestrial and fluviatile shells of North America.
New Harmony Disseminator of Useful Knowledge 2(18): 275 277.
Smith, D.G.
(1980) Goniobasis
virginica (Gastropoda: Pleuroceridae) in the Connecticut
River USA. Nautilus 94:50-54.









